Transformer
Failure Type and Breakdown Causes of The Transformers by CIGRE
Survey done by a CIGRE working group on failures in large power transformer found that about 41 percent failures were due to on-load-tap changers/OLTC and about 19 percent were due to windings. The failure origin were 53 percent mechanical and 31 percent dielectric. On transformer without on-load-tap changers / OLTC, 27 percent of failure were due to the windings, 6 percent were due to magnetic circuit, 33 percent were due to terminals, 17 percent were due to the tank and dielectric fluid, 12 percent were \due to other accessories, and 5 percent were due to the tap changer.
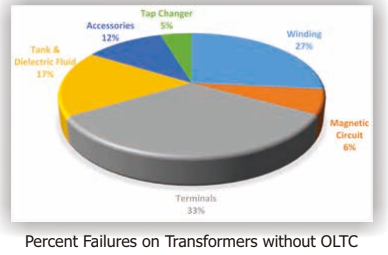
Looking into the failures type and percentage the transformer assessment were concentration in the causes of aging transformer with the following breakdown of causes:
- Dielectric Causes, electrical stress particularly in areas with high electrical field strengths
· Dielectric losses produce of heat
· Decomposition of solid and liquid insulation by partial discharge
· Generation of gases
· Generation of acids and sludge - Electromagnetic Causes, high current (ea. due to short circuits nearby the transformer) produce high mechanical forces
· Deformation of the winding
· Damage to paper insulation (cracks), particularly on aged parts
· Initiation of partial discharge
· Initiation of partial breakdowns - Chemical Causes, organic acids are produced as a result of ageing
· In particular, they affect the paper insulation -> accelerated ageing
· Metals like copper, iron, aluminum and zinc are behaving like catalyst. -> accelerated ageing - Thermal Causes, High currents (ea. due to short circuits nearby the transformer) produce high mechanical forces
· Hysteresis losses in the magnetic core
· Shorted laminates
· Ohmic losses in the windings due the voltage drop
· Dielectric losses in the insulation
· Load changes will cause warming up and cooling down negative influences on the lifetime of the insulation.
· The ageing of the insulation is accelerated if the temperature increase.
Transformer Oil Analysis
Detecting faults to prevent failure with oil analysis
Gas detection periodically in the oil-filled transformers in service can be used as the first indication of a problem in the transformer that may eventually lead to failure if not corrected. Electrical discharges or thermal stresses in the oil or solid insulation, for example, paper pressboard etc, of an oil-filled transformer cause degradation of these materials with the formation of gases of various types.
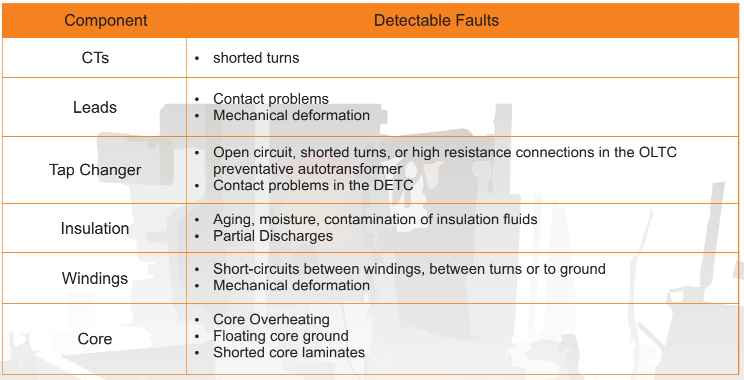
The Failure of transformer can be a devasting and costly experiance. However, it is an unfortunate fact that despite even the most rigorous preventive maintenance program, failures can and will occur. The foregoing classification of failures is admittedly general in nature, but usually sufficient for our claims process. However, in order to prepare an accurate failure scenario, and develop proper recommendations to prevent a recurrence, a more in-depth analysis of the failure is necessary.

How to Sampling Oil Transformer
