Pump Installation
General Description
Pump system and process control involve a wide range of technologies and sciences, and they are used in an unprecedented number of applications. Examples range from the control of heating, cooling, and hot water systems in homes and office to chemical and pump system and process control.
In the Pump System a wide number of variables, from submersible, vacuum, flow and pressure to time and distance, can be sensed simultaneously. All of these can be interdependent variables in a single process requiring complex microprocessor systems for total control. In order to produce a product with consistently high quality, tight process control is necessary
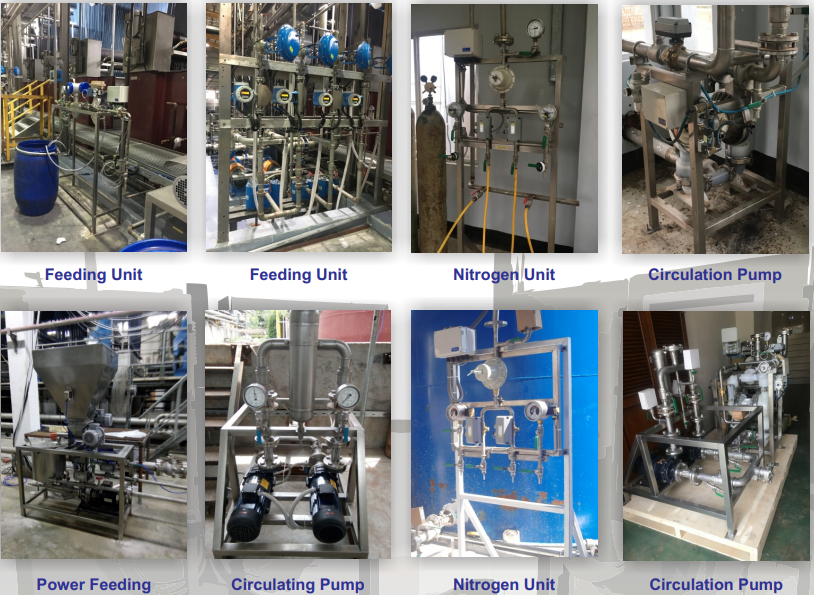

Pump System
SUBMERSIBLE PUMP
A submersible pump, also called an electric submersible pump, is a pump that can be fully submerged in water. The motor is hermetically sealed and close-coupled to the body of the pump. A submersible pump pushes water to the surface by converting rotary energy into kinetic energy into pressure energy. This is done by the water being pulled into the pump: first in the intake, where the rotation of the impeller pushes the water through the diffuser. From there, it goes to the surface.
VACUUM PUMP
A vacuum pump is a device which was invented in 1650 by Otto von Guericke. Its main function is to remove gas molecules from a sealed volume and leave a partial vacuum behind. Basically, it is used to pull out air and gases from a sealed or confined space due to which the space is left out of any gas and air molecules.
WATER PRESSURE PUMP
A pressure pump is a pump with some sort of electrical switch on it which turns the pump off when the system pressure reaches a pre-set point, sometimes this is fixed and sometimes it is adjustable. When your pressure pump is running and a tap on the system is open, the water flows out of the tap

FIRE FIGHTING PUMP
Fire-fighting pumps are mechanical devices consisting of a water pump coupled to an electric motor or an endothermic engine. They are used to move a certain amount of water at a pressure that can extinguish a fire, according to project data. They are used in case of emergency and must be installed in most of the industrial activities.
CIRCULATING PUMP
A circulating pump works by pumping or circulating liquids, gases or slurries in a loop or closed circuit. Their most common application is circulating water in a hydronic cooling or heating system. Since the materials that they pump move around in closed circuits, they do not expend lot of energy. For example, when water is initially pumped upwards, it circulates around a system and eventually returns to its original position. From this point, a pump only needs enough power to counteract the drag or inertia in pipes to propel the water forward efficiently. This process is repeated over and over again.
COOLING WATER PUMP
Cooling water pumps are used for supplying heat exchanger with cooling water. Their flow rate varies depending on the heat flow to be dissipated. The required head is determined by the type of cooling system. A distinction is made between wet cooling and dry cooling processes.

Field Instrument Installation
The instrumentation on a process plant represents a significant capital investment, and the importance of careful handling on site and the exactitude of the installation cannot e overstressed. Correct installation is also important to ensure long-term reliability and to obtain the best results instruments that are capable of higher-order accuracies because of advances in technology. Quality control of the completed work is also an important function.
Installation should be carried out using the best engineering practices by skilled personnel who are fully acquainted with the safety requirements and regulations governing a plant site. Prior to commencement of the work for a specific project, installation design details should be made available, which define the scope of work and the extent of material supply and which give detailed installation information related to location, fixing, piping and wiring. When instruments are received on a job site, it is of the utmost importance that they are unpacked with care, examined for superficial damage, and then placed in a secure store, which should be free from dust and suitably heated.

Preliminary Process
For Process measurement to achieve the targets of safety, accuracy, reliability, and economy, more than measuring equipment is involved. The entire system-from the process fluid characteristics, the ambient conditions, legal and regulatory requirements, and operations/maintenance requirements – must be coordinated to ensure that the equipment can be installed, calibrated, operated, recalibrated, maintained, and if necessary, rebuilt or replaced while meeting the above primary criteria.
This require to survey the site for the installation proposed, and to make any necessary arrengements to have the required lifting and handling equipment, installation tools, any specified components and site services available, to carried out safety and efficient installation.
Collecting Installation Document
Collect each of physical devices is referenced to the associated installation drawings, such as the physical location plans, installation detail (mechanical support, piping and wiring), cable ladder and conduit routing diagrams, and the connection diagram, as a reference for the installation work. The installation document is usually one of many documents from a large database, which also keeps track of calculations, specifications, and procurement documents and may also interface with a three-dimensional CAD model of the plant.
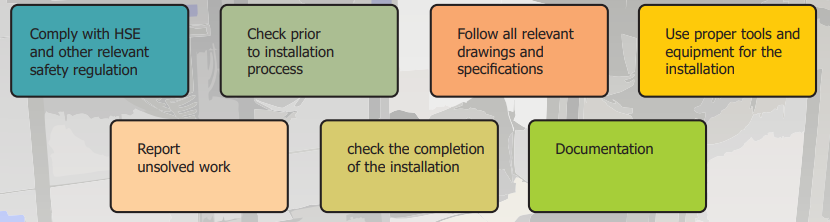
Ensuring Safe Installation
Expecting the work with a maximum of supervision, taking each personal responsibility for own action, quality and accuracy of the work. The installation activity may be carried out as a team effort, and the supervision able to demonstrate a significant personal contribution to the installation activities, in order to satisfy the requirement of standard and safety installation.
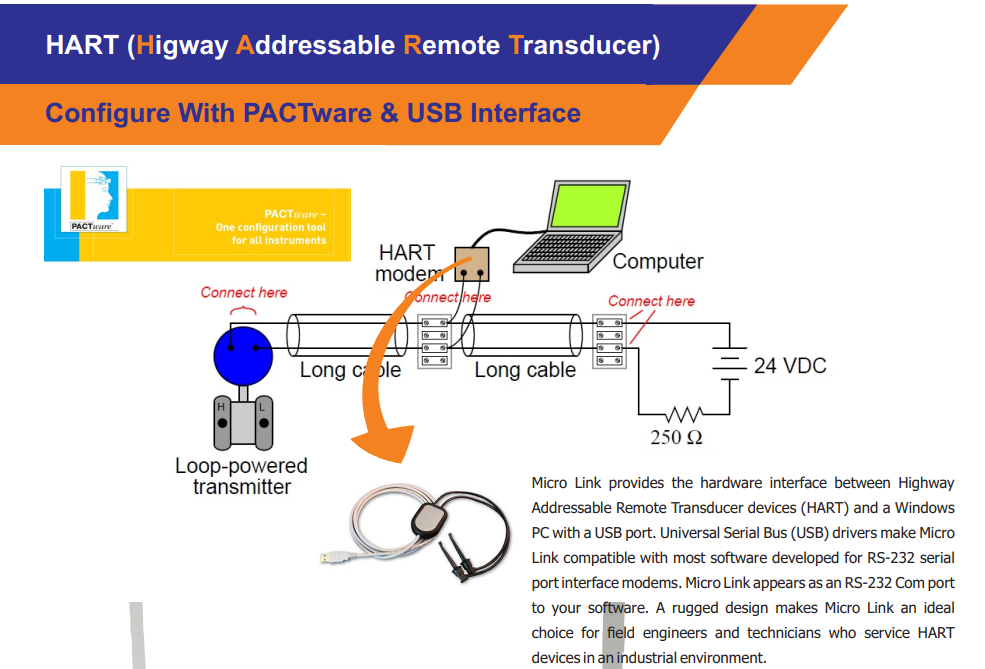
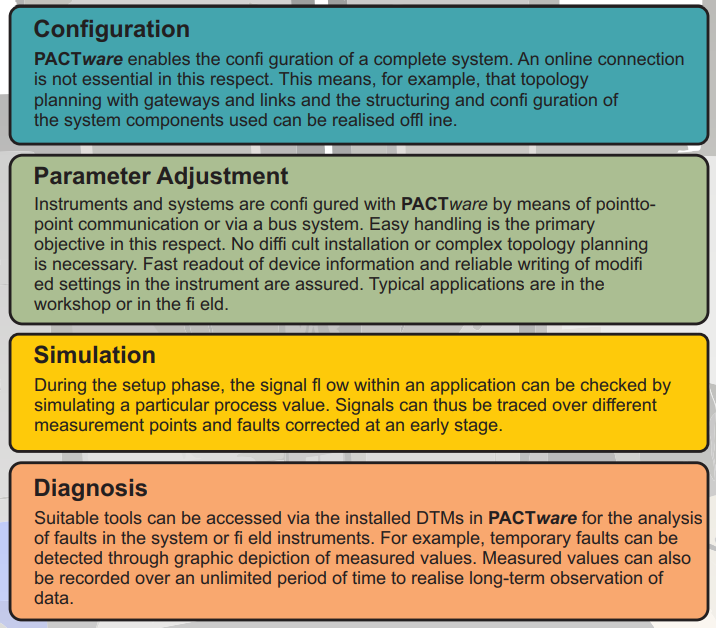
Configuration PACTware

Ensuring Safe Installation
Particular sefety precaution that should be aware such as :
Working in Confined Spaces
Work in confined spaces can cause injuries in any industries, ranging from those involving complex plant through to simple storage. Those victims include not only people working in the confined space but also those who try to rescue them without proper training and equipment.
Some confined spaces are fairly easy to identify, e.g. enclosures with limited openings : Storage tanks, tunnels, enclosed drains, reaction vessels, silos. Others may be less obvious, but can be equally dangerous, for example: Chamber, pipe, flues, hatches.
A “competent person” should be appointed to carry out a risk assessment of the conditions and the work and activities to be conducted in the confined space, and identify the necessary safety precautions to be taken according to the findings to avoid posing hazards to workers. The “competent person” should make recommendations on safety precautions to be taken having regard to the nature of the confined space, the associated risk and the work involved.
Working in High Place
In many industries, employees are required to deal with many risks associated with working in high places. Safety should be the top priority in these kinds of jobs and thus should be taken seriously. High-altitude falls are generally the biggest single cause of casualties in the workplace contributing to more than one-third of total workplace fatalities every year. Falls are debilitating, they are deadly and one must be prepared to protect their employees. So fall protection is required whenever there is a need for working at heights.

Type of Field Instrument
Pressure-Sensing Device
Pressure-sensing devices are chosen for pressure range, overload requirements, accuracy, temperature operating range, line-of-sight reading, or electrical signal, and response time. in some applications there are other special requirements. Parameters, such as hysteresis and stability, should be obtained from the manufacturers specifications.
Level-Sensing Device
Level-sensors detect the level of liquids and other fluids and fluidized solids, including slurries, granular materials, and powders that exhibit an upper free surface. There are many physical and application variables that affect the selection of the optimal level.
Flow-Sensing Device
Flow sensors are used to measure both gas and liquid flows in many monitoring and control applications. Flow can be various defined (e.g, mass, volume, laminar, turbulent). The amount of a substance flowing (mass flow) is usually the one of interest. Flow rate is typically obtained by first measuring the velocity of a fluid in a pipe, duct, or othre structure and then multiplying by the known cross-sectional area at the point of measruement
Temperature-Sensing Device
Temperature-sensors is a device, typically, a thermocouple or RTD, that provides for temperature measurement through an electrical signal. A thermocouple (T/C) is made from two dissimilar metals that generate electrical voltage in direct proportion to changes in temperature. An RTD (Resistance Temperature Detector) is a variable resistor that will change its electrical resistance in direct proportion to changes in temperature in a precise, repeatable and nearly linear manner.
